Details of DPV and References
DPV NO: 350 December 1989
Family: Alphaflexiviridae
Genus: Potexvirus
Species: Pepino mosaic virus | Acronym: PepMV
Pepino mosaic virus
Renate Koenig Institut für Viruskrankheiten der Pflanzen, Biologische Bundesanstalt für Land- und Forstwirtschaft, D-3300 Braunschweig, Germany
D.-E. Lesemann Institut für Viruskrankheiten der Pflanzen, Biologische Bundesanstalt für Land- und Forstwirtschaft, D-3300 Braunschweig, Germany
R.A.C. Jones Western Australian Department of Agriculture, Baron Hay Court, South Perth 6151, Western Australia
Contents
- Introduction
- Main Diseases
- Geographical Distribution
- Host Range and Symptomatology
- Strains
- Transmission by Vectors
- Transmission through Seed
- Transmission by Grafting
- Transmission by Dodder
- Serology
- Nucleic Acid Hybridization
- Relationships
- Stability in Sap
- Purification
- Properties of Particles
- Particle Structure
- Particle Composition
- Properties of Infective Nucleic Acid
- Molecular Structure
- Genome Properties
- Satellite
- Relations with Cells and Tissues
- Ecology and Control
- Notes
- Acknowledgements
- Figures
- References
Introduction
Described by Jones et al. (1980).
A virus with filamentous particles c. 510 x 12.5 nm. It is transmitted by inoculation with sap to solanaceous species and a few in other families. No vector is known but the virus readily spreads through plant contact. The virus has been found so far only in the coastal region of Peru.
Main Diseases
Solanum muricatum (pepino) is the only natural host known. Infected plants show a distinct yellow mosaic (Fig. 1).
Geographical Distribution
Reported only from the coastal region of Peru (Jones et al., 1980).
Host Range and Symptomatology
The experimental host range is mainly restricted to solanaceous plants (Jones et al., 1980) but symptomless local infections develop in Tetragonia expansa and Cucumis sativus. Some potato cultivars develop systemic mosaic and/or severe systemic necrosis but others are infected symptomlessly.
-
Diagnostic species
- Datura metel
and D. stramonium. Strong systemic mosaic and, in young leaves, systemic necrotic patching, spotting and flecking (Fig. 3). Inoculated and lower non-inoculated leaves may later develop irregular expanding necrotic patches resulting in generalized leaf necrosis. Young leaves that develop later are infected symptomlessly. - Nicotiana debneyi. Strong systemic mosaic with some necrotic spots,
rings and lines
(Fig. 4).
Expanding necrotic patches and generalized necrosis of inoculated and lower non-inoculated
leaves, as with Datura spp., especially under shaded conditions.
- N. glutinosa. Distinct yellowish mosaic on tip leaves 4-5 days after inoculation followed both in older leaves and in leaves produced afterwards by generalized milder mosaic symptoms (Fig. 2). Generalized necrosis of inoculated and lower non-inoculated leaves, as with Datura spp., especially under shaded conditions.
Propagation species
- Nicotiana glutinosa, N. occidentalis.
Assay species
- Nicotiana glutinosa.
No local lesion host is known.
Strains
None reported.
Transmission by Vectors
No vector known.
Transmission through Seed
No report.
Serology
The virus is a moderately good immunogen. Antisera with titres of 1/512 in slide precipitin tests are readily obtained. Precipitates are floccular.
Relationships
The virus is a typical member of the potexvirus group. Serological relationships were detected with narcissus mosaic and cactus X viruses, but not with eight other potexviruses (Jones et al., 1980).
Stability in Sap
In sap of N. glutinosa, the thermal inactivation point (10 min) was between 60 and 65°C, dilution endpoint 10-4 to 10-5, and infectivity was retained for at least 3 months at 20°C (Jones et al., 1980).
Purification
Mince 100 g infected N. glutinosa or N. occidentalis leaves in 25 ml of a solution at pH 7.8 containing 0.065 M disodium tetraborate, 0.435 M boric acid, 0.2% ascorbic acid and 0.2% sodium sulphite. Filter homogenate through muslin and centrifuge expressed sap at low speed. To 1 vol. of the supernatant fluid add 0.15 vol. 0.4% silver nitrate and leave at room temperature for c. 3 h. Centrifuge at low speed and add 4% (w/v) of polyethylene glycol M. Wt 6000 to the supernatant fluid. Leave at 4°C overnight. Centrifuge at low speed, resuspend the pellets in a solution at pH 7.8 containing 0.065 M disodium tetraborate, 0.435 M boric acid, 0.5 M urea and 0.1% mercaptoethanol. Subject the virus to two cycles of differential centrifugation and resuspend the final pellets in 0.01 M Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.0.
Properties of Particles
No information.
Particle Structure
The particles (Fig. 5) are flexuous filaments measuring mostly c. 510 x 12.5 nm. Cross-banding of particles is not seen as clearly as with potato virus X.
Particle Composition
Nucleic acid: No information.
Protein: In SDS-polyacrylamide gels the coat protein migrates usually as two bands with estimated M. Wt of 26.6 x 103 and 23.2 x 103. The smaller protein is probably a degradation product of the larger one.
Relations with Cells and Tissues
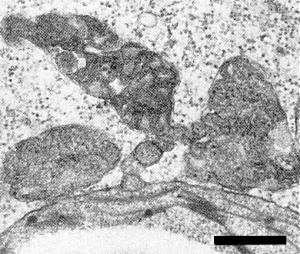
In the cytoplasm of leaf cells of N. glutinosa arrays of the filamentous particles often form inclusions which appear whorled (Fig. 6) or banded (Fig. 7). Scattered virus particles are rarely seen. Accumulations of proliferated rough endoplasmic reticulum occur in the cytoplasm (Fig. 6, lower part) and small vesicles containing dsRNA-like fibrils are produced at the tonoplasts of infected cells (Fig. 6, upper part; see also Francki et al., 1985). Mitochondria are sometimes fragmented and have an unusually dense matrix (Fig. 8; Jones et al., 1980).
Notes
Pepino may also be naturally infected by at least two other viruses with filamentous particles: a potyvirus which causes a chlorotic mosaic (Jones et al., 1980) and a carlavirus (Jones et al., 1980; Thomas et al., 1980) which provisionally was named pepino latent virus because it infects pepino symptomlessly (Thomas et al., 1980). This carlavirus was later shown to be an isolate of the Andean strain of potato virus S (Dolby & Jones, 1988). The potyvirus was shown be wild potato mosaic virus (C.E. Fribourg, personal communication).
Acknowledgements
The senior author’s work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Figures

Virus particle from crude extract of N. glutinosa, negatively stained with uranyl acetate. Bar represents 100 nm.

Ultrathin section of infected N. glutinosa leaf parenchyma cells: whorled particle aggregates and accumulations of endoplasmic reticulum in the lower part and small, tonoplast-associated vesicles in the upper part; bar represents 1 µm.
References list for DPV: Pepino mosaic virus (350)
- Dolby & Jones, Ann. appl. Biol. 112: 231, 1988.
- Francki, Milne & Hatta, An Atlas of Plant Viruses, Vol. II, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 248 pp., 1985.
- Jones, Koenig & Lesemann, Ann. appl. Biol. 94: 61, 1980.
- Thomas, Mohamed & Fry, Ann. appl. Biol. 95: 191, 1980.